Discover how our phishing simulations turn your employees into active defenders of your organization.

Human Risk Management
How to create a strong password
No time to read? Listen instead:
Does your password contain “1234”? Do you think the name of your favorite hobby, partner, or pet is an easy-to-remember but hard-to-crack password? We’ve all been there. In our fast-paced environment, we want to create strong passwords that are memorable and secure, but we don’t have enough time to create or remember long, complex versions.
With the average person using around 100 passwords to protect their accounts, it’s not a surprise that we continuously reuse the same ones and have a hard time coming up with unique alternatives. Despite our best efforts, Verizon’s 2023 Data Breach Investigations Report reveals that humans can be more predictable than we like to think, with 86% of data breaches originating from stolen credentials.
Despite the alarming statistics, it’s safe to say that most people know the importance of having a strong password. However, turning the advice of making them complex and unpredictable into reality is challenging for many. Is “DanielandStacy76” harder to crack than “hgYhy23”? Is using the same one for different accounts secure enough? Keep reading to understand what a good password looks like and how to create strong, memorable ones without taxing your mental energy.
Dos and don’ts when creating a secure password
Establishing a secure online presence is no small feat, especially when creating a robust password. Let’s decode the dos and don’ts of creating a password that is a resilient key to your digital world:
Tip 1: Make your password at least 12 characters long
The longer and more complex a password is, the harder it is for a malicious actor to crack it through brute-force or guessing methods. A password with only a few characters can be deciphered relatively quickly, even when special characters, numbers, and uppercase letters are used. However, a password that contains at least 12 characters exponentially increases the number of potential combinations, making it significantly more difficult for a cybercriminal to successfully guess or crack. For even better security, we recommend going over 12 characters, further reducing the chances of a hack and thus protecting your personal information, digital assets, and online privacy more effectively.
If you struggle to make a good password, password managers like 1Password, LastPass, or Dashlene can generate secure passwords with the number of characters you request. Some of the password manager companies also have free online password generators you can use to create more secure passwords.
Tip 2: Avoid using sequential numbers or letters
Avoid using sequential letters or numbers in passwords (like “123456” and “abcdef”) because these are predictable patterns that significantly reduce the complexity and security of your password. They are among the first combinations an attacker tries when attempting to crack your password using common tactics like dictionary attacks or brute-force attacks. And many automated hacking tools have these sequences pre-programmed into their algorithms, making a password with such patterns easy to break.
Tip 3: Use a combination of letters (lower and upper case), numbers, and symbols
Incorporating a mixture of lowercase and uppercase letters, numbers, and symbols in your password is key to boosting your password security. Just like a longer password raises the number of possible combinations a hacker must attempt to crack it, including different types of characters also increases the complexity.
Tip 4: Don’t use names or words found in the dictionary
Using words or names that are listed in the dictionary can critically compromise your password’s security. This is because one common method cyberattackers use to crack passwords is a dictionary attack, which is a type of brute-force attack. In a dictionary attack, the attacker uses a program that systematically enters every word in a dictionary, or a list of commonly used passwords, as a guess to try and crack your password. If your password has these common words or names, it has a higher risk of being cracked during these attacks.
Tip 5: Don’t use personal information – especially if you have shared it online
In the interconnected digital world we live in, hackers are always a step away. They, like us, use technology and social media to their advantage. Your public communications, posts, tweets, and other shared details – unless marked private – can be mined by cyberintruders. These digital spaces provide a wealth of information about you, including your profession, family members’ names, favorite hobbies, or even your pet’s name. Now, consider the foundation of your online security – your passwords. If they contain any of these details, your accounts will be as exposed like an open book. Remember that your digital footprint is far-reaching, far more than you may realize. And it’s there, in plain sight, accessible to anyone with the will to exploit it.
Tip 6: Don’t use the same password again
Reusing passwords across multiple platforms is a significant security risk. The main reason is that if one of your accounts is compromised in a data breach, cybercriminals often try the same username and password combination on other platforms. This practice, known as ‘credential stuffing,’ has proven to be worryingly successful in recent breaches like the PayPal one, where 35,000 accounts were affected.
Tip 7: Use multi-factor authentication
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of protection beyond just a username and password. Even if an attacker successfully steals or guesses your password, they will still need to bypass the additional layer of security provided by MFA to gain access to your account. This additional layer might be something you know, such as passwords, something you have like physical tokens, or something you are, such as fingerprints or facial IDs. The more factors used to confirm identity, the more difficult it becomes for an attacker to gain unauthorized access.
MFA can also be a useful tool for detecting unauthorized access attempts. If you receive a text message with a verification code when you’re not trying to log into your account, this is a clear indication that someone else is attempting to access your account. This gives you the opportunity to take immediate action, such as changing your password, enabling additional security measures, or contacting the platform’s security support to report the unauthorized access attempt.
Most commonly used passwords
In the virtual battlefield against sophisticated cybercriminals, choosing a straightforward, predictable password is equivalent to leaving your front door unlocked.
A startling reality is that many users believe they are creating original passwords, thinking their choices are unique and thus secure. However, human behavior tends to fall into patterns, and the choice of passwords is no different. The result is that these seemingly unique passwords may end up being as common as “123456” or “password,” making them easy targets for cybercriminals. This ease of access enables potential intruders to breach accounts in moments, underscoring the urgent need for greater awareness and more secure password practices. Below are 10 of the most common passwords in 2023. If you spot your password in this list, it’s a signal for you to update it immediately.

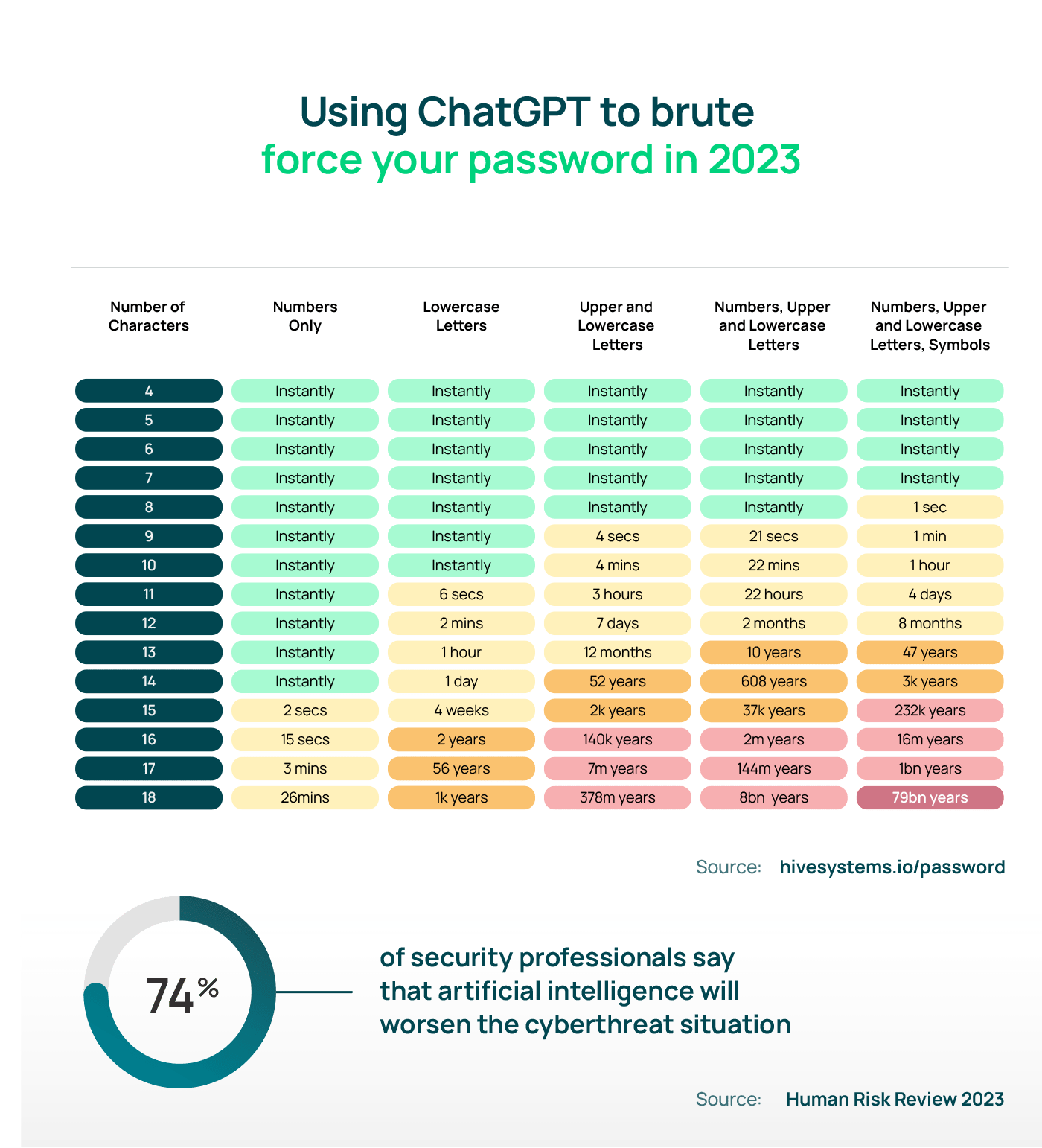
Timeframe for a breach – How quickly can hackers decipher your password?
The time it takes to crack a password varies greatly, depending on many factors. These factors range from the password complexity and the encryption mechanism used for password security to the technology, resources, and tools that hackers have at their disposal.
Password length and complexity
A password’s complexity and length directly influence its vulnerability to hacking. Longer and more complex passwords translate into more combinations a hacker needs to test. However, the accelerating pace of tech innovations is a game-changer and is now tipping the scales toward hackers.
Take an eight-character password that includes uppercase and lowercase letters. In 2020, cracking such a password might have been a 22-minute game for a hacker. Fast forward to 2023, and this same task is a mere 28-second sprint. The message is clear: as time passes, so does the hacker’s prowess at decoding our defenses. As the digital clock ticks, escalating our password’s complexity becomes not just a smart move but a necessary countermeasure to the relentless advances in hacking techniques.
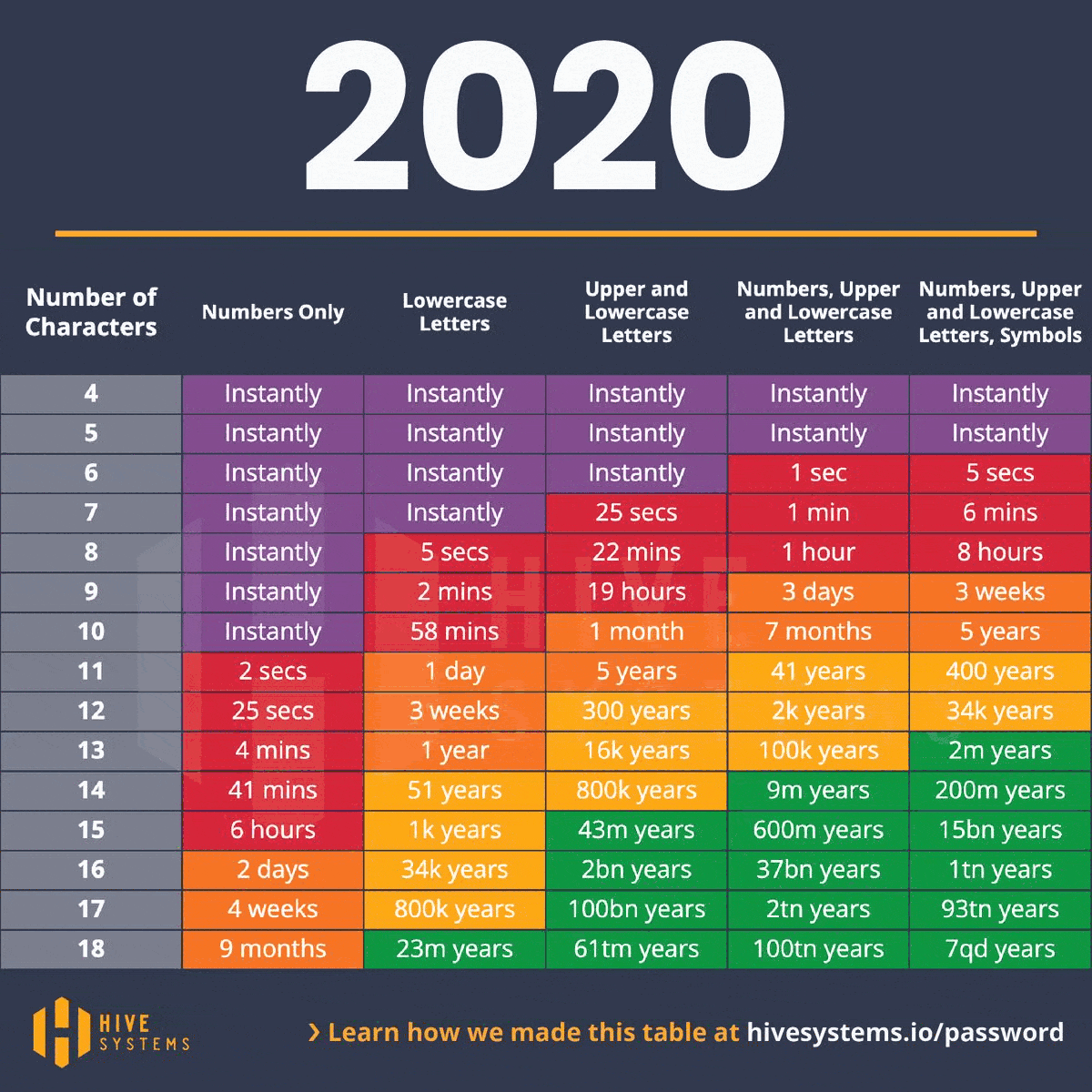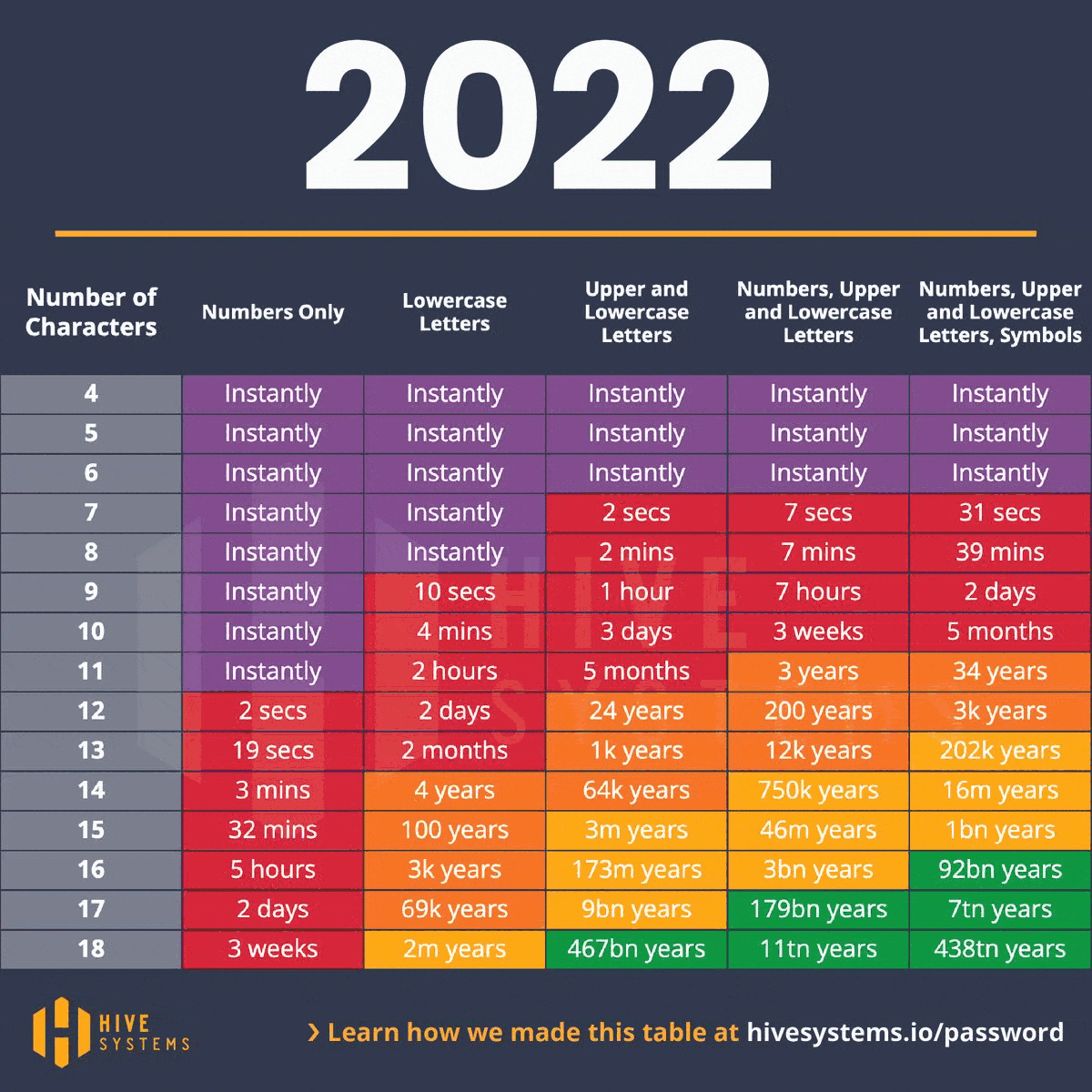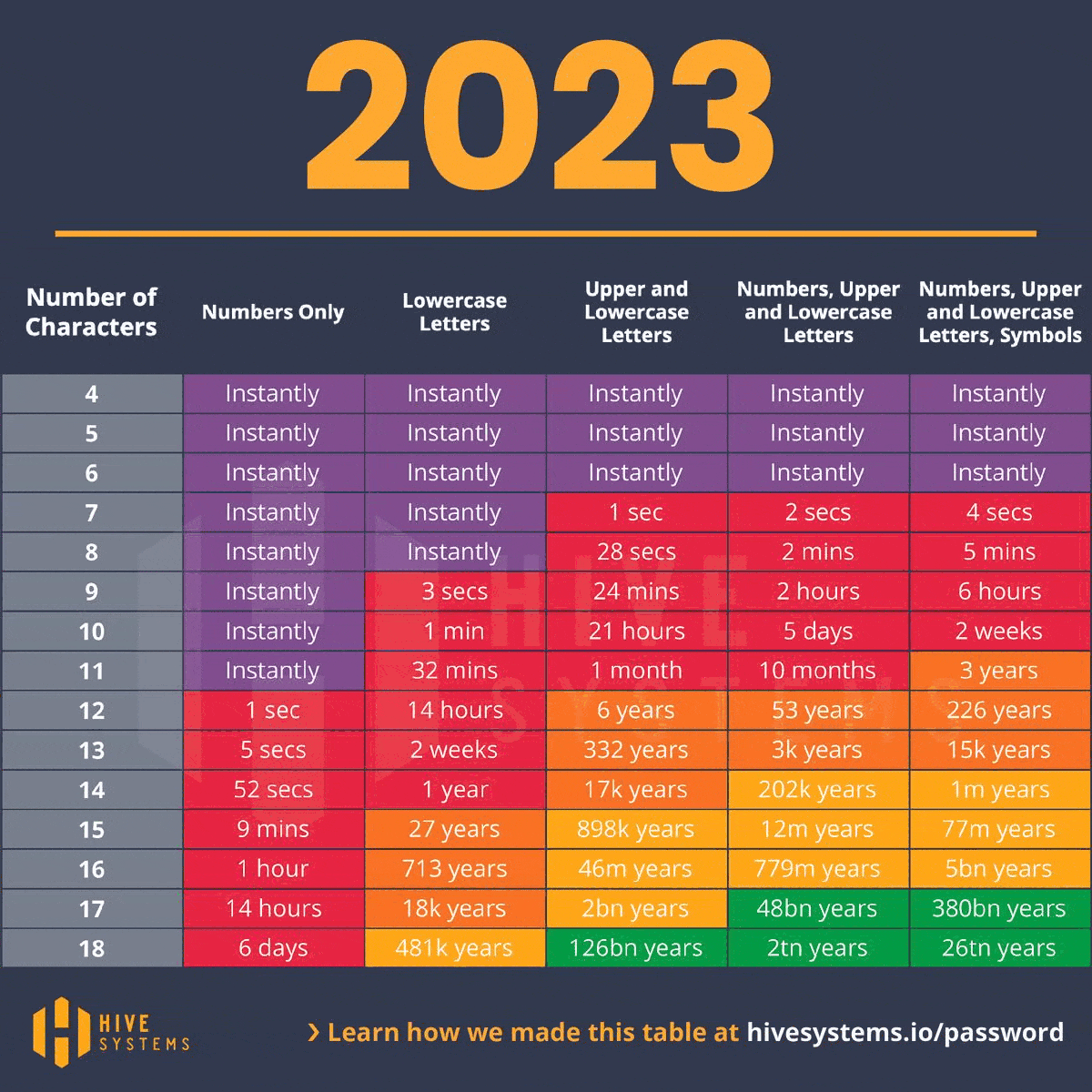
The hackers’ toolbox
Within the high-stakes arena of cyber security, the technological capabilities and resources at a hacker’s disposal drastically impact the rate they can decode passwords. As the landscape of cybercrime continually evolves, hackers consistently equip themselves with cutting-edge software and hardware, accelerating the password-cracking process. These tools have the power to launch brute-force or dictionary attacks at an astonishing pace, sifting through an immense number of potential password combinations in the blink of an eye.
These days no tool has gained as much traction among cyberattackers as ChatGPT. Its impressive language-generation abilities provide cybercriminals with a unique advantage, creating countless combinations of usernames and passwords that can be used in brute-force attacks. ChatGPT technology has dramatically accelerated the pace of password cracking, often reducing the time to mere seconds. Consider a password composed of nine characters, incorporating numbers and lowercase and uppercase letters – once a formidable task to crack, it now stands vulnerable in 21 seconds thanks to the capabilities of ChatGPT.
Secure or not?: Distinguishing strong from weak passwords
You’ve already learned valuable tips on strengthening your security, and we’ve seen how quickly hackers crack weak passwords, but you might be wondering what a strong one looks like. To help you visualize this, we provide examples of strong passwords and some weak ones to illustrate the varying degrees of protection they can offer.
| Password | Security level | Reason |
| ird2yyzRbHXkV}xXqm3RX*F-oWX2,} | Highest | More than 12 characters Contains special characters, numbers, upper and lower case No consecutive numbers or letters No words from the dictionary |
| mnYIW2ZZWhg96HnUHpYj | High | Lacks special characters |
| taxggkwuj6vt | Medium | Lacks uppercase and special characters |
| @Thomas42 | Low | Contains words from the dictionary Less than 12 characters |
| abc12345 | Lowest | Less than 12 characters Lacks special characters and upper case Consecutive numbers and letters |
Remembering strong passwords: Best practices
Let’s face it: The main reason we don’t use long and complex – yet secure – passwords is the daunting task of remembering them. However, there are techniques that can help us overcome this challenge.
One technique is cleverly using patterns and substitutions to create memorable yet secure passwords. First, select a memorable phrase or quote that resonates with you. Take the first letter of each word in the chosen phrase and combine them to form the foundation of your password. For example, if your favorite quote from a book is “The only way out of the labyrinth of suffering is to forgive,” your password foundation would be “Towootlositf.” To increase the complexity, replace certain letters with similar-looking symbols or numbers. For example, you could replace “o” with “0,” (zero) “s” with “$,” and “i” with “!” to create “T0w00tl0$!tf.” To further increase the complexity, add a few numbers that mean something to you. For example, the page where the quote is in the book. Your final password would be “T0w00tl0$!tf47.”
If you don’t want to worry about how to remember your passwords, consider using a password manager that gives you the convenience of having just one master password that grants you access to all your other passwords with a single click. These trustworthy tools securely store your passwords and provide seamless access through a master password or biometric authentication. Not only does this save you time and spare you from the mental strain of memorization, but it also offers added benefits, such as password generators to create strong, unique passwords and password breach detection to alert you if any of your accounts may have been compromised. Remember to type your master password regularly to strengthen your muscle memory and reduce the risk of forgetting it.
How to avoid being hacked
In today’s digital landscape, hackers’ methods to acquire our credentials are vast and ever-evolving. From the age-old practice of eavesdropping in public spaces to the more sophisticated techniques involving powerful computing tools for brute-force attacks, cyberintruders are constantly honing their skills. By gaining insight into their tactics, we empower ourselves to safeguard our digital identities and strengthen our online security.
Phishing: Don’t give out your credentials
Phishing and social engineering tactics are hackers’ preferred methods to gain access to your credentials. By instilling a sense of fear, urgency, or authority, they trick you into entering your username and password. Once they do that, they use your credentials for a wide range of purposes, including financial fraud, impersonation, and credential stuffing.
Remember that phishing techniques go well beyond email-based attacks. Cybercriminals are adept at exploiting various communication channels, including SMS, seemingly harmless messages within messaging apps, and even direct phone calls.
Brute-force attacks: How to prevent them
Brute-force attacks capitalize on the vulnerability of short, predictable, and weak passwords by systematically trying numerous combinations using automated computer systems. However, there are effective measures you can adopt to avoid the brute-force hacking process:
- Use a strong password by following the tips mentioned in this article.
- Use multi-factor authentication (MFA). Even if the hacker gains access to your credentials, they would not be able to access your account without the second authentication factor.
- Limit the number of unsuccessful login attempts that can be made during account authentication.
- Require your employees to use CAPTCHA to add another layer of security.
- Use an IP denylist to identify and block sources of malicious traffic.
- Keep software and firmware updated to avoid hackers exploiting vulnerabilities.
Watch out in public places
Public places can serve as a lucrative hunting ground for cybercriminals. With numerous individuals and devices connected to the internet, the risk of falling victim to malicious activities becomes more prominent, especially when using public networks. Unsecured networks, particularly those lacking password protection, heighten the danger. When connecting to these networks, such as free public Wi-Fi at airports and cafes, it is crucial to employ a VPN (Virtual Private Network) to safeguard your login credentials from eavesdroppers.
In addition to securing your online activities, it’s important to be mindful of age-old techniques that still pose a significant threat. Simple yet effective methods like shoulder surfing, where individuals observe your screen as you enter credentials, remain a genuine concern. Mitigate this risk by using privacy screens on your devices, preventing unwanted prying eyes from gaining access to sensitive information.
Make phishing attacks miss the mark
Spreading the word of password security: How to protect your organization from credential theft
Following good password-creating tips like making them complex, long, and with various different characters provides an extra level of security to your accounts. However, in an era of evolving cyber threats where hackers constantly upgrade their digital arsenals, the best practices for creating robust passwords will keep evolving to combat them. A password considered secure yesterday might be easily decipherable today, underscoring the importance of ongoing cyber security awareness training.
SoSafe’s Awareness Training modules on how to create a strong password are adapted to your employees’ needs and are continuously refreshed with the latest insights and information from the cyber security industry. Moreover, the Content Management feature of our learning platform provides an effective tool for sharing your password policy with your employees and tracking acceptance, helping you reinforce your organization’s cyber defenses.



