VPN
What is a VPN?
A VPN, or Virtual Private Network, is like a secure tunnel for your internet connection. It works by encrypting your data and routing it through a server located in a different place, essentially making it appear as if your internet connection is coming from that server’s location. It’s a smart way to keep your online actions hidden from unwanted eyes, offering a shield of privacy and security. This is particularly important when you’re on public Wi-Fi or accessing sensitive information, as it keeps your personal data under lock and key, away from the reach of cybercriminals.
With the surge in remote work, they’ve become more than just a privacy tool. They’re now an essential job requirement for many remote employees. But before we focus on how they can be used in companies, let’s explore how VPNs work.

VPN explained: How it works to safeguard your data
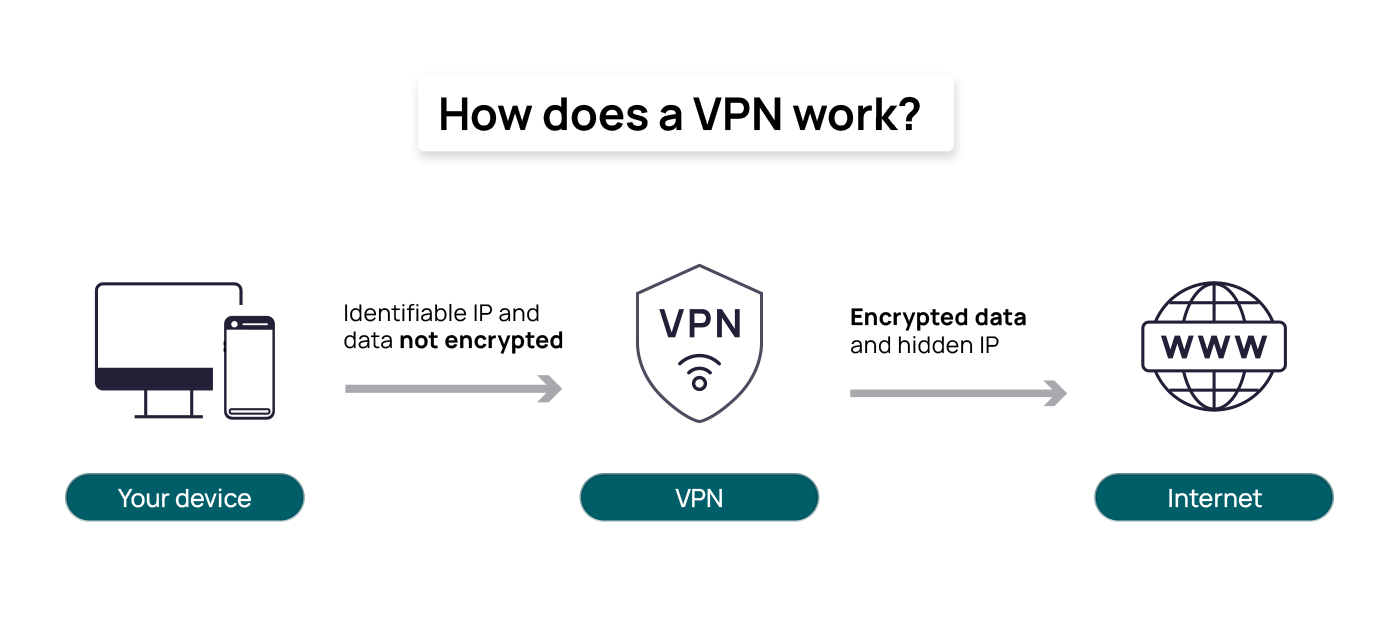
A regular internet connection involves direct communication between your device and the websites or online services you access. When you connect to the internet without a VPN, your data travels through your internet service provider’s servers, potentially exposing your online activities to surveillance.
VPNs add an additional layer of security. When you initiate a VPN connection, a secure tunnel is created between your device (computer, smartphone, etc.) and the VPN server. This tunnel encrypts your internet data, which means it’s converted into a code that can only be deciphered with the appropriate decryption key. Your internet traffic is directed through this VPN server before reaching the broader internet. This server can be located in a different geographical location, like another city or country.
As your data flows through this VPN server, it remains encrypted to prevent anyone who might intercept your data from understanding or making use of it. In other words, the VPN server effectively acts as a middleman for your internet requests.
Suppose you’re in a coffee shop and want to access your online banking. Without a VPN, your data travels through the coffee shop’s public Wi-Fi network, potentially exposing your sensitive information to hackers. But with a VPN, you connect to your VPN service, which encrypts all your data. This encrypted data is then sent through a secure tunnel to a VPN server located elsewhere. The VPN server then acts on your behalf to request your online banking page. The response received by the VPN server is decrypted there and then sent back to your device.
This process ensures your online activities are protected and private. Even if you’re connected to the coffee shop’s public Wi-Fi network, your data is secure. Potential eavesdroppers on the public network will only see encrypted data passing between your device and the VPN server.
The main benefits of using a VPN
A VPN offers many benefits that can enhance your online experience and safeguard your digital life. Here are the main advantages:
- Online privacy: A VPN encrypts your internet connection, ensuring your online activities remain private. It conceals your IP address and browsing history, making it challenging for anyone, including hackers and advertisers, to track your online behaviour.
- Security on public Wi-Fi: When you connect to public Wi-Fi networks, you’re often at risk of data interception by cybercriminals. A VPN provides a secure tunnel for your data, protecting it from potential threats and ensuring your sensitive information remains confidential.
- Anonymous browsing: VPNs make it difficult for websites to trace your online activity back to you. This anonymity can help you maintain privacy while browsing the web.
- Enhanced security: In addition to encryption, VPNs often offer additional security features like ad-blocking and protection against malware and phishing attempts, further safeguarding your online experience.
- Remote access: For businesses, VPNs facilitate secure remote access to company networks and data. This is particularly valuable in a world where remote work and telecommuting are increasingly common.
- Network scalability: VPN servers facilitate access for multiple employees and remote workers simultaneously. They also support cloud-based applications, providing secure access via the VPN tunnel. This scalability allows businesses to easily accommodate more users and grant them access to the required resources.
- Privacy from ISPs: VPNs prevent your internet service provider (ISP) from monitoring and selling your online data to advertisers, preserving your online privacy.
- Avoid bandwidth throttling: Some internet service providers limit the speed of specific online activities, like streaming and gaming. VPNs can help bypass these restrictions, ensuring a smooth online experience.
- Reduce costs: In traditional onsite setups where companies have their own servers, maintaining them and addressing performance or security issues consumes time and internal resources. With a VPN, these responsibilities are transferred to the service provider, who can manage the infrastructure more efficiently and with reduced costs.
Virtual Private Network types
To fully understand the power and versatility of VPNs, it’s essential to delve into the various types of VPNs. Exploring different VPN models, along with their unique features and use cases, can help you decide on the most appropriate VPN solution for your specific needs.
Remote Access VPN
A Remote Access VPN creates a secure connection for individual users, typically remote employees and clients, who need to access their organisation’s network from external locations. The VPN encrypts their data and routes it through a VPN server provided by the organisation, which acts as a gateway to the corporate network.
Some of the providers of this type of VPN include PureDome (by PureVPN), NordLayer, Windscribe StrikeForce, Surfshark, GoodAccess, and OpenVPN Access Server.
Site-to-Site VPN
A Site-to-Site VPN connects multiple geographically dispersed office locations within an organisation securely. These VPNs establish connections by configuring network devices like routers or firewalls at each site. When data needs to travel between these sites, it’s encrypted and sent over the internet, where the configured devices on each end handle encryption and decryption.
There are two types of Site-to-Site VPNs: Extranet and Intranet VPN.
- Extranet VPN enables external clients, such as business partners and suppliers, to access an organisation’s network securely. Users from outside the organisation connect by installing a VPN client provided by the organisation or through a web portal.
- Intranet-based VPNs provide secure internal access within an organisation’s premises. Employees within the organisation connect to this type of VPN from their devices, typically when they are on the organisation’s premises. To connect, users often need to use the organisation’s network infrastructure and possibly authenticate with their credentials.
Perimeter 81, Juniper, Cisco Dynamic Multipoint VPN, and NordLayer are popular Site-to-Site VPN providers.
Personal VPN
A Personal VPN is a secure and private tunnel for users who want to protect their online activities. It initiates a process of data encryption, converting the user’s data into an unreadable code routed through a VPN server located in a different geographic location. The server acts as a protective shield around the user’s information, preventing eavesdroppers, hackers, or the internet service provider from monitoring or tracking online activities.
Some popular examples of personal VPN providers include NordVPN, Atlas VPN, Norton Secure VPN, ExpressVPN, CyberGhost, IPVanish, and others.
Mobile VPN
A Mobile VPN extends the secure tunnel concept to mobile devices, allowing users to safeguard online activities while using smartphones and tablets. It operates similarly to a regular VPN but is optimised for mobile platforms, ensuring privacy and security for users on the go. With data encryption and routing through a designated VPN server, a Mobile VPN shields sensitive information from potential threats, providing a protective layer against unauthorized access, tracking, and monitoring.
Notable providers of Mobile VPN services include NordVPN, ExpressVPN, Atlas VPN, Norton Secure VPN, CyberGhost, and IPVanish, among others.

What is a VPN protocol, and does it matter when choosing a VPN?
VPN protocols are the backbone of secure and private online communication. They dictate how data is encapsulated, transmitted, and decrypted within the virtual tunnels created by VPNs. These protocols are the key elements that safeguard sensitive information, defend against cyber threats, and enable remote access to secure networks.
The table below provides a comparison of different VPN protocols, highlighting their primary applications, performance, and security features.
| VPN protocol | Main use | Speed | Compatibility and ease of use | Reliability and security level |
| OpenVPN | Security and compatibility | High | High | High |
| PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol) | General use | High | High | Low (due to vulnerabilities) |
| L2TP (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol) | Security with slightly reduced speed | Medium | High | Medium-High |
| IPsec (Internet Protocol Security) | Corporate environments | Medium-High | Medium (managed by Admins) | High |
| L2TP/IPsec (Combined Protocol) | Enhanced security with moderate performance | Medium | High | Medium-High |
| SSTP (Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol) | Secure, stable connection on windows | High | High | High |
| IKEv2 (Internet Key Exchange version 2) | Mobile devices and remote access | High | High | Medium-High |
| WireGuard | Balanced speed and security | High | Medium (due to Newness) | High |
The most suitable choice depends on your specific requirements and priorities regarding data sensitivity, device compatibility, and performance expectations. Based on these criteria, the VPN you choose may be free or paid, each providing different features and security levels.
How to choose a good VPN service
A good VPN should provide comprehensive features to ensure your online security and privacy. Here’s what to look for in a reputable VPN provider:
- Speed: Look for VPN services with good speed and performance, especially if you’ll be streaming, gaming, or downloading large files.
- Strong protocols: Look for a provider that uses industry-standard protocols with advanced encryption that will ensure your data is safe from prying eyes.
- IP address protection: A quality provider should offer options for rerouting your IP address. Shared IP addresses group multiple users under one IP, enhancing your anonymity. Quick and easy server switching lets you choose your preferred location from various options.
- Many server locations: The performance of your VPN can be impacted by the number and location of the provider’s servers. More servers in various locations, both near and far from you, result in faster speeds and smoother connections. A broad server network ensures you can easily switch to an IP address from a specific region.
- Zero-log policy: A zero-log policy means the VPN provider doesn’t log or store any data that passes through their servers, ensuring your online activities remain private. They may retain basic information like your email address and payment details for account management, but your usage logs, connection logs, and IP addresses should not be recorded or stored.
- Kill switch: A kill switch is a crucial feature that immediately cuts off your internet connection if the VPN connection is disrupted, ensuring your identity remains protected.
- Mobile compatibility: For a secure mobile experience, choose a provider offering mobile VPN support, including switching to secure protocols like IKEv2/IPsec when using public Wi-Fi networks or cellular data.
- Authentication: Look for VPN providers that offer multiple authentication options to enhance security. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) requires users to provide two or more verification factors to gain access to a resource.
- Customer support: A reliable VPN provider should offer accessible, responsive, and knowledgeable customer support to assist with any issues or questions.
- Pricing: Avoid free VPNs, which often have limitations and potential privacy concerns. Opt for a paid VPN provider with higher-quality technology and infrastructure, stronger security, and a commitment to user privacy.
- Reviews: Read reviews from reputable tech sites and user testimonials to gauge the reputation of the VPN service.
What’s the difference between a free VPN and a paid VPN?
Much like a spectrum of services available today, VPN applications come in two models, free and premium paid versions, each with a unique set of perks. Making an informed decision between free and paid options means understanding the full suite of features and benefits each one brings to the table.
Free VPNs provide a secure and encrypted tunnel for your internet traffic to pass through without requiring any financial commitment. This tunnel ensures that your data is protected and cannot be easily intercepted or accessed by third parties, such as hackers or your internet service provider. However, free VPNs have limitations like reduced speed and bandwidth, limited server locations, and potentially less robust security and privacy features. Some free VPNs rely on advertising or data collection to generate revenue, impacting user privacy. Additionally, customer support may be minimal or non-existent, making it challenging for users to receive assistance or resolve technical issues promptly.
Paid VPN services offer a more comprehensive and reliable solution for online privacy and security. They have many server locations, unlimited device connections, and additional security and privacy features like ad-blocking, split tunneling, and multi-hop connections. Paid VPNs often implement advanced features like strong encryption and a strict no-logs policy, ensuring user data remains private and protected. In contrast to free VPNs, paid options rely on subscription fees rather than collecting and monetizing user data. This means they are oriented toward safeguarding user privacy. Moreover, they offer dedicated customer support, including live chat, email, and phone support, making it easier to resolve issues or obtain answers to questions promptly.
Is using a VPN legal?
The legality of VPN usage can differ depending on where you are and how you use it. In democratic countries across Europe and the US, VPNs are usually unrestricted and used for many legitimate reasons. However, in some countries, VPN use is more controlled, and government-approved VPN services are the legal choices.
Countries like China, Russia, Oman, Egypt, UAE, Turkey, Iran, and India have restrictions on VPN use, while in countries like North Korea, Iraq, Turkmenistan, and Belarus, VPN usage is not just restricted; it’s outright prohibited. The consequences of using VPNs in these countries can range from penalties to criminal offenses, so stay informed about the local laws when traveling or residing in such regions.
Knowing the laws and regulations regarding VPNs in your location is essential. Always use a VPN for lawful and ethical purposes and avoid activities that break the law. Also, opt for a reputable VPN service that respects user privacy and follows legal standards. While VPNs offer enhanced privacy and security, responsible and legal use is the key.
What’s the difference between a VPN and a proxy?
A VPN and a proxy are like two different masks you can put on when you’re online, and they both help you hide your real face (or, in this case, your real online identity). However, they work a bit differently.
A proxy serves as an intermediary between a user’s device and the internet, routing traffic through its server to change the user’s IP address. This function is mostly application-specific, affecting traffic from a certain browser or application. Proxies are useful for basic anonymity tasks, such as bypassing geo-restrictions or accessing blocked content, but they do not encrypt data. This makes them less secure and not ideal for handling sensitive information or ensuring complete online privacy.
In contrast, a VPN not only changes the user’s IP address but also encrypts all internet traffic from the device. Operating at the system level, VPNs secure all data, regardless of the application or browser in use. This comprehensive encryption offers a significant security advantage, protecting against data breaches, surveillance, and cyber threats. VPNs are the preferred choice for robust online security and privacy, particularly when accessing the internet over unsecured public Wi-Fi networks or handling sensitive information.

Does a VPN protect you from all cyber threats?
The primary functions of a VPN are to secure your data through encryption and provide online anonymity. However, VPNs are not a one-stop solution for all online threats. There are some things they cannot protect from, namely the following:
- Malware and viruses: While a VPN is an excellent guard against data interception and it can offer some protection against malware and viruses, it won’t protect your device from all threats. You’ll need dedicated antivirus software for higher protection against these threats.
- Scams and phishing: VPNs cannot act as your personal fraud detectors. They cannot shield you from social engineering or prevent phishing attempts. Staying vigilant and exercising caution when navigating the digital landscape is crucial to avoiding these traps.
- Password security: Protecting your passwords is your responsibility, as VPNs don’t enforce or ensure the strength of your passwords. Using unique and secure passwords for your various online accounts is essential to protect your online presence.
- Legal consequences: Engaging in illegal online activities, such as hacking or cybercrime, can lead to legal consequences, even if you’re using a VPN. VPNs are not a shield against the law. They provide privacy, not immunity from legal action.
A VPN is a potent ally for securing your online adventures, but it’s most effective when combined with other security measures, such as antivirus software and smart online practices.
Are VPNs recommended for businesses?
VPNs are great for businesses looking to strengthen their online security and streamline network operations. Encrypted tunnels can significantly enhance data protection, making them indispensable in a world where cyber threats are ever-present. However, it’s important to be aware of some of the challenges that businesses may encounter when using VPNs, such as:
- Security concerns: VPNs can introduce security risks if not set up or managed correctly. For example, if a hacker gains access to the VPN, they could potentially access the company’s internal network.
- Monitoring: VPNs can make monitoring network activity more challenging, as they can obscure where traffic is coming from. This could potentially make it harder to spot suspicious activity.
- Scalability: As businesses grow, the number of employees needing VPN access can increase significantly. This places demands on network infrastructure, potentially requiring additional servers and bandwidth to accommodate the user surge. The maintenance overhead also grows as the business expands, necessitating more effort to manage user credentials, access policies, and monitor traffic effectively.
- Complexity: Setting up and configuring a VPN can be complex, often requiring skilled IT professionals to ensure proper network management. This complexity can lead to additional costs for hiring or training IT staff. Moreover, the intricacies of VPNs can result in more frequent technical issues, requiring robust support structures for quick problem resolution.
- Performance: VPNs introduce encryption and routing, which can cause latency or slowdowns in data transfer. Businesses reliant on real-time applications may find this latency detrimental. Additionally, VPNs can place demands on available bandwidth, potentially impacting users’ experiences, especially during peak usage times.
- User experience: Users may encounter difficulties connecting to the VPN, particularly if multi-factor authentication or complex credentials are required. VPN connections can sometimes drop, requiring users to reconnect, disrupting workflows, and leading to frustration.
Despite these challenges, the advantages of VPNs in protecting sensitive data and providing secure access to company resources often outweigh the drawbacks. With the right approach and support, businesses can effectively harness the power of VPNs to safeguard their digital operations.
How VPNs and security awareness training complement each other
In today’s digital landscape, VPNs stand out as a practical tool for securing online activities. However, the true efficacy of these security measures is unlocked through a holistic understanding of cyber security principles. This is precisely where the significance of security awareness training comes into play. SoSafe, leveraging a sophisticated behavioural science approach, offers comprehensive security awareness training designed to equip employees with the knowledge and insights necessary for the effective utilization of tools such as VPNs.
The heart of SoSafe’s training lies in its gamified lessons, carefully designed to educate employees on the critical importance of safeguarding login credentials – the virtual keys that grant access to VPNs and corporate resources. These engaging lessons are delivered in a customizable and personalized learning format, transforming the often-mundane process of learning about VPNs and other cyber security topics into an enjoyable and memorable experience. The result is not just enhanced awareness but a tangible improvement in retention, ensuring that the knowledge gained is not only understood but actively applied in real-world scenarios.
Beyond fostering cyber security awareness, our training modules cultivate a shift toward a data security culture, where employees become active contributors to the larger goal of data protection. This reflects a commitment to creating a resilient cyber security environment where every individual plays a crucial role in fortifying the digital defence mechanisms of your organisation.


















